Australian tiger snakes have “hit the jackpot” because prey cannot evolve resistance to their venom.
articles
How Continents Were Recycled
Researchers from Germany and Switzerland have used computer simulations to analyse how plate tectonics have evolved on Earth over the last three billion years. They show that tectonic processes have changed in the course of the time, and demonstrate how those changes contributed to the formation and destruction of continents. The model reconstructs how present-day continents, oceans and the atmosphere may have evolved.
How cytoplasm ''feels'' to a cell's components
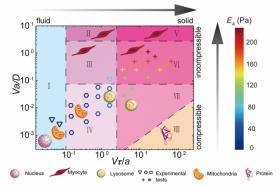
Under a microscope, a cell’s cytoplasm can resemble a tiny underwater version of New York’s Times Square: Thousands of proteins swarm through a cytoplasm’s watery environment, coming together and breaking apart like a cytoskeletal flash mob.
Organelles such as mitochondria and lysosomes must traverse this crowded, ever-changing cytoplasmic space to deliver materials to various parts of a cell.
Now engineers at MIT have found that these organelles and other intracellular components may experience the surrounding cytoplasm as very different environments as they travel. For instance, a cell’s nucleus may “feel” the cytoplasm as a fluid, honey-like material, while mitochondria may experience it more like toothpaste.
Methane Hydrate is not a Smoking Gun in the Arctic Ocean
Clathrate (hydrate) gun hypothesis stirred quite the controversy when it was posed in 2003. It stated that methane hydrates – frozen water cages containing methane gas found below the ocean floor – can melt due to increasing ocean temperatures.
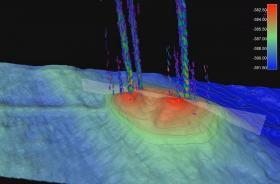
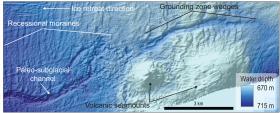
Hidden river once flowed beneath Antarctic ice
Antarctic researchers from Rice University have discovered one of nature’s supreme ironies: On Earth’s driest, coldest continent, where surface water rarely exists, flowing liquid water below the ice appears to play a pivotal role in determining the fate of Antarctic ice streams.
The finding, which appears online this week in Nature Geoscience, follows a two-year analysis of sediment cores and precise seafloor maps covering 2,700 square miles of the western Ross Sea. As recently as 15,000 years ago, the area was covered by thick ice that later retreated hundreds of miles inland to its current location. The maps, which were created from state-of-the-art sonar data collected by the National Science Foundation research vessel Nathaniel B. Palmer, revealed how the ice retreated during a period of global warming after Earth’s last ice age. In several places, the maps show ancient water courses — not just a river system, but also the subglacial lakes that fed it.
Once invincible superbug squashed by 'superteam' of antibiotics
The recent discovery of E. coli carrying mcr-1 and ndm-5 — genes that make the bacterium immune to last-resort antibiotics — has left clinicians without an effective means of treatment for the superbug.
But in a new study, University at Buffalo researchers have assembled a team of three antibiotics that, together, are capable of eradicating the deadly bacterium. The groundbreaking research was recently published in mBio, a journal for the American Society of Microbiology.