Almost all of the turtles living in a southern California lake died following a large fire and years of drought, according to a new U.S. Geological Survey report published in the journal Knowledge and Management of Aquatic Ecosystems.
articles
U.S. had 2nd warmest year to date and 9th warmest March on record
As a transition between winter and spring in the U.S., March is the kind of month where just about any type of weather can happen. Coming off a very warm February 2017, many of us were tricked into thinking spring had arrived. However, an Arctic plunge of frigid air plowed into the nation’s midsection in mid-March, dashing hopes of an early spring and freezing plants as far south as Florida.
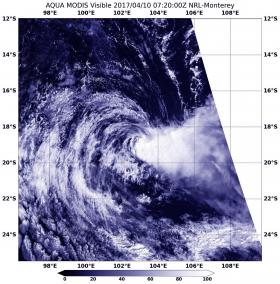
NASA Catches Tropical Cyclone Ernie Being Blown Apart
NASA's Aqua satellite provided a birds-eye view of Tropical Cyclone Ernie as it was being battered by strong vertical wind shear and torn apart.
Hubble Spots Auroras on Uranus
This is a composite image of Uranus by Voyager 2 and two different observations made by Hubble — one for the ring and one for the auroras.
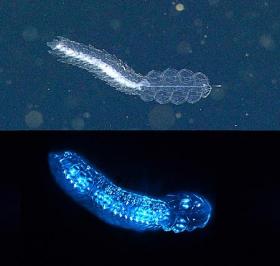
We all glow together— New study shows that three quarters of deep-sea animals make their own light
Ever since explorer William Beebe descended into the depths in a metal sphere in the 1930s, marine biologists have been astounded by the number and diversity of glowing animals in the ocean. Yet few studies have actually documented the numbers of glowing animals at different depths. In a new study in Scientific Reports, MBARI researchers Séverine Martini and Steve Haddock show that three quarters of the animals in Monterey Bay waters between the surface and 4,000 meters deep can produce their own light.
Catastrophic 'anti-infestation' logging threatens US National Forests
A fresh wave of logging is hitting America's national forests, writes Brett Haverstick. But this time it's all for the sake of 'forest health' and 'fire prevention'. It might look like industrial clear-cutting to you and me, but really, it's in a good cause. And if the forests and precious ecosystems they harbor just happen to perish in the process ... well ain't that just too bad?