When a forest fire decimated more than 3,000 acres of Rice University-owned timberland in 2011, biogeochemist Carrie Masiello saw a silver lining in the blackened trees.
articles
U of T neuroscientist on how advances in AI may help us better understand why neurons are shaped the way they are
The shape of our neurons may indicate our brains actually employ a type of learning, dubbed “deep learning,” that was developed to drive artificial intelligence, or AI, applications, a University of Toronto researcher has found.
Exposure to Air Pollution Just Before or After Conception Raises Risk of Birth Defects
Women exposed to air pollution just prior to conception or during the first month of pregnancy face an increased risk of their children being born with birth defects, such as cleft lip or palate or abnormal hearts.
Canola Oil Linked to Worsened Memory and Learning Ability in Alzheimer's Disease, Temple Researchers Report
Canola oil is one of the most widely consumed vegetable oils in the world, yet surprisingly little is known about its effects on health. Now, a new study published online December 7 in the journal Scientific Reports by researchers at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University (LKSOM) associates the consumption of canola oil in the diet with worsened memory, worsened learning ability and weight gain in mice which model Alzheimer’s disease. The study is the first to suggest that canola oil is more harmful than healthful for the brain.
How a Wayward Arctic Current Could Cool the Climate in Europe
For millennia, the Beaufort Gyre — a massive wind-driven current in the Arctic Ocean — has been regulating climate and sea ice formation at the top of the world. Like a giant spinning top, the gyre corrals vast amounts of sea ice. Trapped in this clockwise swirl, the ice has historically had more time to thicken than it generally does in other parts of the Arctic Ocean, where currents such as the Trans Polar Drift transport the ice into the warmer north Atlantic more rapidly. In this way, the Beaufort Gyre — located north of Alaska and Canada’s Yukon Territory — has helped create the abundant layers of sea ice that, until recently, covered large parts of the Arctic Ocean year-round.
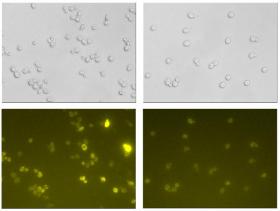
Yeast can be engineered to create protein pharmaceuticals
It took several years, but a research team headed by Professor Jens Nielsen at Chalmers University of Technology has finally succeeded in mapping out the complex metabolism of yeast cells. The breakthrough, recently published in an article in Nature Communications, means a huge step forward in the potential to more efficiently produce protein therapies for diseases such as cancer.