Fuels that are produced from nonpetroleum-based biological sources may become greener and more affordable, thanks to research performed at the University of Illinois’ Prairie Research Institutethat examines the use of a processing catalyst made from palladium metal and bacteria.
Fuels that are produced from nonpetroleum-based biological sources may become greener and more affordable, thanks to research performed at the University of Illinois’ Prairie Research Institutethat examines the use of a processing catalyst made from palladium metal and bacteria.
Biofuels are made from renewable materials such as plants or algae, and offer an alternative to petroleum-based sources. However, many biofuels are costly to produce because the precursor product, bio-oil, must be processed before it is sent to the refinery to be turned into liquid fuel. Illinois Sustainability Technology Center researcher B.K. Sharma and his co-authors have identified and tested a new processing method.
“Bio-oil forms from the same chemical reaction that forms petroleum,” Sharma said. “But what takes millions of years naturally in the ground takes only minutes in the lab using a process that is very similar to pressure cooking.”
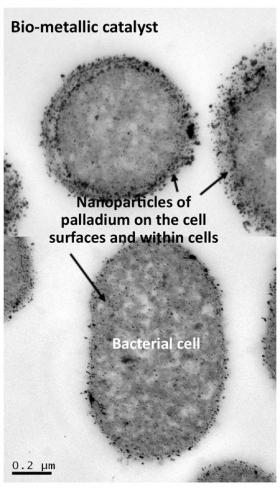
Published in the journal Fuel, their findings point to a cheaper, more environmentally friendly and renewable catalyst for processing that uses common bacteria and the metal palladium, which can be recovered from waste sources such as discarded electronics, catalytic converters, street sweeper dust and processed sewage.
Read more at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Image: A photomicrograph of the palladium and bacteria catalyst. (Credit: Image courtesy Lynne Macaskie)