Researchers have discovered a new reaction mechanism that could be used to improve catalyst designs for pollution-control systems to further reduce emissions of smog-causing nitrogen oxides in diesel exhaust.
Researchers have discovered a new reaction mechanism that could be used to improve catalyst designs for pollution-control systems to further reduce emissions of smog-causing nitrogen oxides in diesel exhaust.
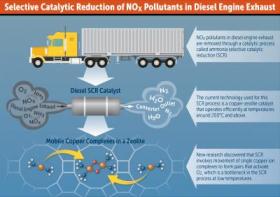
The research focuses on a type of catalyst called zeolites, workhorses in petroleum and chemical refineries and in emission-control systems for diesel engines.
New catalyst designs are needed to reduce the emission of nitrogen oxides, or NOx, because current technologies only work well at relatively high temperatures.
“The key challenge in reducing emissions is that they can occur over a very broad range of operating conditions, and especially exhaust temperatures,” said Rajamani Gounder, the Larry and Virginia Faith Assistant Professor of Chemical Engineering in Purdue University’s Davidson School of Chemical Engineering. “Perhaps the biggest challenge is related to reducing NOx at low exhaust temperatures, for example during cold start or in congested urban driving.”
Read more at Purdue University
Image: This diagram depicts a new reaction mechanism that could be used to improve catalyst designs for pollution-control systems for diesel exhaust. (Credit: Purdue University photo/Maureen Lifton)