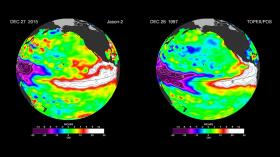
The current strong El Niño brewing in the Pacific Ocean shows no signs of waning, as seen in the latest satellite image from the U.S./European Ocean Surface Topography Mission (OSTM)/Jason-2 mission.
El Niño 2015 has already created weather chaos around the world. Over the next few months, forecasters expect the United States to feel its impacts as well.
The latest Jason-2 image bears a striking resemblance to one from December 1997, by Jason-2's predecessor, the NASA/Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES) Topex/Poseidon mission, during the last large El Niño event. Both reflect the classic pattern of a fully developed El Niño.
The current strong El Niño brewing in the Pacific Ocean shows no signs of waning, as seen in the latest satellite image from the U.S./European Ocean Surface Topography Mission (OSTM)/Jason-2 mission.
El Niño 2015 has already created weather chaos around the world. Over the next few months, forecasters expect the United States to feel its impacts as well.
The latest Jason-2 image bears a striking resemblance to one from December 1997, by Jason-2's predecessor, the NASA/Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES) Topex/Poseidon mission, during the last large El Niño event. Both reflect the classic pattern of a fully developed El Niño. The images can be viewed at:
http://sealevel.jpl.nasa.gov/elnino2015/index.html
The images show nearly identical, unusually high sea surface heights along the equator in the central and eastern Pacific: the signature of a big and powerful El Niño. Higher-than-normal sea surface heights are an indication that a thick layer of warm water is present.
El Niños are triggered when the steady, westward-blowing trade winds in the Pacific weaken or even reverse direction, triggering a dramatic warming of the upper ocean in the central and eastern tropical Pacific. Clouds and storms follow the warm water, pumping heat and moisture high into the overlying atmosphere. These changes alter jet stream paths and affect storm tracks all over the world.
This year's El Niño has caused the warm water layer that is normally piled up around Australia and Indonesia to thin dramatically, while in the eastern tropical Pacific, the normally cool surface waters are blanketed with a thick layer of warm water. This massive redistribution of heat causes ocean temperatures to rise from the central Pacific to the Americas. It has sapped Southeast Asia's rain in the process, reducing rainfall over Indonesia and contributing to the growth of massive wildfires that have blanketed the region in choking smoke.
El Niño is also implicated in Indian heat waves caused by delayed monsoon rains, as well as Pacific island sea level drops, widespread coral bleaching that is damaging coral reefs, droughts in South Africa, flooding in South America and a record-breaking hurricane season in the eastern tropical Pacific. Around the world, production of rice, wheat, coffee and other crops has been hit hard by droughts and floods, leading to higher prices.
The latest satellite image of Pacific sea surface heights from Jason-2 (left) differs slightly from one 18 years ago from Topex/Poseidon (right). In Dec. 1997, sea surface height was more intense and peaked in November. This year the area of high sea levels is less intense but considerably broader. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Read more at JPL-NASA