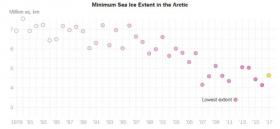
Famous for its weather forecasts, the Old Farmer’s Almanac has published its predictions for the coming year—but don’t believe everything you read.
The folksy pocket-sized magazine has been a regular go-to for farmers and other fans during fall harvest season since it first began publishing in 1792. As cosy and comforting as pumpkin pie, it offers everything from home remedies to food recipes—but the long-range weather predictions that fill many of its pages are nothing but pure guesswork, said a University of Alberta weather modelling expert.