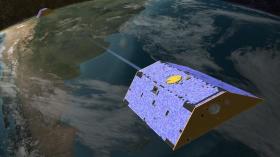
The twin satellites that have been critical in measuring the world’s melting ice sheets for 15 years will soon shut down — months before their replacement is launched into orbit, NASA announced, creating a gap in the ice data record that has been instrumental in studying the impacts of global warming.
articles
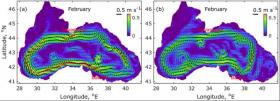
Black Sea Water Temperatures May Buck Global Trend
Average surface temperatures of the Black Sea may not have risen, according to the surprising results of a new study from the JRC.
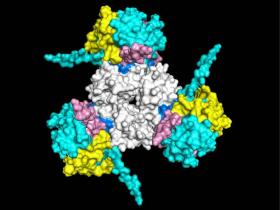
Scientists Discover Genetic Markers for Severe Form of Multiple Sclerosis
Scientists have uncovered two related cytokines and associated genetic markers that may explain why some people develop progressive multiple sclerosis, or MS. The study, led by researchers at OHSU in Portland, Oregon, and Yale University, point the way toward developing the first-ever treatment to prevent progressive forms of the disease.
Heather Kulik: Innovative modeling for chemical discovery
Without setting foot from her office, Heather Kulik, the Joseph R. Mares '24 Career Development Assistant Professor of Chemical Engineering, is charting unknown worlds. Her discoveries plumb “vast regions of chemical space,” she says, a domain comprised of combinations of chemical elements that do not yet exist. “Best estimates indicate that we have likely made or studied only about 1 part in 10 to the 50th of that chemical space,” she says.
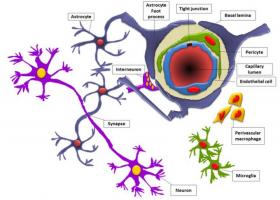
New Model May Help Overcome the Brain's Fortress-Like Barrier
Scientists have helped provide a way to better understand how to enable drugs to enter the brain and how cancer cells make it past the blood brain barrier.
Exposure to Pet and Pest Allergens During Infancy Linked to Reduced Asthma Risk
Children exposed to high indoor levels of pet or pest allergens during infancy have a lower risk of developing asthma by 7 years of age, new research supported by the National Institutes of Health reveals. The findings, published September 19 in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, may provide clues for the design of strategies to prevent asthma from developing.