At least 100,000 military veterans who served in the 1990-1991 Gulf War were exposed to chemical weapons, released into the air after the United States bombed an ammunition depot in Khamisiyah, Iraq. Today, many are still suffering from Gulf War Illness, a mysterious, multi-symptom disease that experts believe is linked to organophosphate nerve agents sarin and cyclosarin.
At least 100,000 military veterans who served in the 1990-1991 Gulf War were exposed to chemical weapons, released into the air after the United States bombed an ammunition depot in Khamisiyah, Iraq. Today, many are still suffering from Gulf War Illness, a mysterious, multi-symptom disease that experts believe is linked to organophosphate nerve agents sarin and cyclosarin.
A new paper by researchers at Drexel University sheds light on the neurological consequences of exposure to low-levels of these nerve agents and suggests that drugs like tubacin could treat some of the toxins’ neurological effects. The results were recently published in the journal Traffic.
To model Gulf War Illness, the researchers treated cultures of human and rat neurons with an organophosphate called diisopropyl flurophosphate, which is an analog of sarin. They also pretreated the neurons with stress hormones to better mimic the stressors of war.
- See more at Drexel University
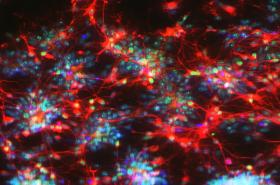
Image reveals a nucleus and two neuronal markers, validating the conversion of adult blood cells that have been “reprogrammed” into pluripotent cell lines and then differentiated into neurons. (Credits: Peter Baas Laboratory)