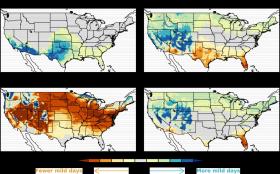
As scientists work to predict how climate change may affect hurricanes, droughts, floods, blizzards and other severe weather, there's one area that's been overlooked: mild weather. But no more.
NOAA and Princeton University scientists have produced the first global analysis of how climate change may affect the frequency and location of mild weather - days that are perfect for an outdoor wedding, baseball, fishing, boating, hiking or a picnic. Scientists defined "mild" weather as temperatures between 64 and 86 degrees F, with less than a half inch of rain and dew points below 68 degrees F, indicative of low humidity.