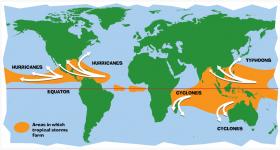
Hurricanes are the most violent storms on Earth. They form near the equator over warm ocean waters. Actually, the term hurricane is used only for the large storms that form over the Atlantic Ocean or eastern Pacific Ocean.
articles
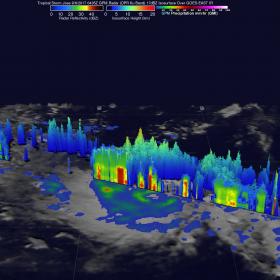
NASA Finds Jose Strengthening into a Hurricane
The Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM core satellite has been providing rainfall rates and cloud heights in tropical cyclones, and recently found towering thunderstorms that indicated strengthening in Tropical Storm Jose. Those "hot towers" were an indication the storm was strengthening and it later became a hurricane.
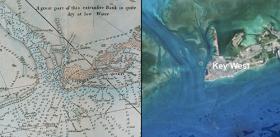
Eighteenth century nautical charts reveal coral loss
Centuries-old nautical charts, mapped by long-deceased sailors to avoid shipwrecks, have been used by modern scientists to study loss of coral reefs.
Researchers develop cheaper, faster test for E. coli in drinking water
Researchers at the University of Waterloo have invented a fast, affordable way for developing communities to test their drinking water for potentially deadly E. coli.
Unlike current tests that cost about $70 and can take up to three days to get back from the lab, the Waterloo invention uses paper strips similar to those in litmus tests to produce results in less than three hours at a cost of 50 cents.
First measurements of iodine in the Arctic reveal questions about air pollution
New measurements of molecular iodine in the Arctic show that even a tiny amount of the element can deplete ozone in the lower atmosphere.
Unprecedented levels of nitrogen could pose risks to Earth's environment
Human production of fixed nitrogen, used mostly to fertilize crops, now accounts for about half of the total fixed nitrogen added to the Earth both on land and in the oceans.