NASA scientists are once again on the hunt for greenhouse gases in the sky.
articles
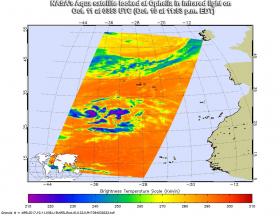
Tropical Storm Ophelia Appears as a Comma in NASA Imagery
Infrared imagery from NASA’s Aqua satellite showed powerful thunderstorms around the center of Tropical Storm Ophelia with a band of thunderstorms stretching to the southwest, giving the storm the appearance of a comma.
Tracking the Viral Parasites of Giant Viruses over Time
In freshwater lakes, microbes regulate the flow of carbon and determine if the bodies of water serve as carbon sinks or carbon sources. Algae and cyanobacteria in particular can trap and use carbon, but their capacity to do so may be impacted by viruses. Viruses exist amidst all bacteria, usually in a 10-fold excess, and are made up of various sizes ranging from giant viruses, to much smaller viruses known as virophages (which live in giant viruses and use their machinery to replicate and spread.)
Climate change may accelerate infectious disease outbreaks
Aside from inflicting devastating natural disasters on often vulnerable communities, climate change can also spur outbreaks of infectious diseases like Zika , malaria and dengue fever, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus.
Establishing interdisciplinary approaches to agriculture and fundamental biological processes
From optimizing food production to feed a growing population to discovering the fundamental behaviors and processes of biopolymers, faculty in the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering (CEE) are leveraging the interdisciplinary nature of the department to establish two new, innovative projects.
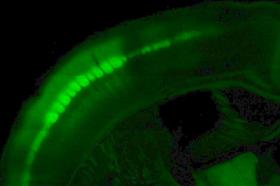
USC research could lead to new ways of treating stroke and spinal cord injuries
It’s a touchy subject — literally. Samuel Andrew Hires, assistant professor of biological sciences, wants to know how the brain learns to understand what we’re touching. Understanding how this works could one day be a boon for people who have suffered a stroke or spinal cord injury.