NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a night-time image of Tropical Cyclone Carlos using infrared light that showed the storm was being stretched out. Carlos is being adversely affected by the Westerlies.
articles
Pre-eclampsia deaths are avoidable
Pregnancy in the UK has never been safer, say scientists from King's College London writing in the latest edition of The Lancet.
Scientists estimate solar nebula's lifetime
About 4.6 billion years ago, an enormous cloud of hydrogen gas and dust collapsed under its own weight, eventually flattening into a disk called the solar nebula. Most of this interstellar material contracted at the disk’s center to form the sun, and part of the solar nebula’s remaining gas and dust condensed to form the planets and the rest of our solar system.
Litter Levels in the Depths of the Arctic are On the Rise
The Arctic has a serious litter problem: in just ten years, the concentration of marine litter at a deep-sea station in the Arctic Ocean has risen 20-fold. This was recently reported in a study by researchers at the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI).
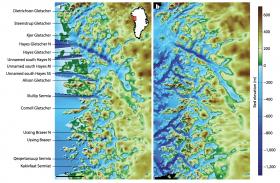
UCI, NASA reveal new details of Greenland ice loss
Less than a year after the first research flight kicked off NASA’s Oceans Melting Greenland campaign, data from the new program are providing a dramatic increase in knowledge of how Greenland’s ice sheet is melting from below. Two new research papers in the journal Oceanography, including one by UCI Earth system scientist Mathieu Morlighem, use OMG observations to document how meltwater and ocean currents are interacting along Greenland’s west coast and to improve seafloor maps used to predict future melting and sea level rise.
Research suggests wearing police uniform changes the way brain processes information
New research from a team of cognitive neuroscientists at McMaster suggests that simply putting on a uniform, similar to one the police might wear, automatically affects how we perceive others, creating a bias towards those considered to be of a low social status.