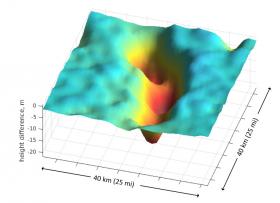
The energy supply to Longyearbyen, midway between continental Norway and the North Pole, is a hot topic in the climate debate.
Longyearbyen is the largest settlement and the administrative centre of Svalbard, a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. Today, Longyearbyen obtains its electric power and district heating from its coal power plant, the only one in Norway.