Farmers earn more profits when there is demand for corn for biofuel instead of for food only. This can lead some to convert grasslands and forests to cropland. This conversion, also called indirect land use change, can have large-scale environmental consequences, including releasing stored carbon into the atmosphere. To penalize the carbon emissions from this so-called indirect land use change, the USEPA and California Air Resources Board include an indirect land use change factor when considering the carbon savings with biofuels for their compliance with the federal Renewable Fuel Standard or California’s Low-Carbon Fuel Standard.
articles
The Clue to Next Years Flu Strain Could be Inside You
Sometimes, a little snot goes a long way. And not just in the physical, stretchy sense. Today, some decade-old snot collected from the sinuses of cancer patients revealed a new technique to forecast how flu evolves.
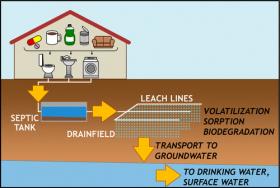
Septic systems are a major source of emerging contaminants in drinking water
A new analysis shows that septic systems in the United States routinely discharge pharmaceuticals, consumer product chemicals, and other potentially hazardous chemicals into the environment. The study, published June 15 in the journal Environmental Science & Technology, is the most comprehensive assessment to date of septic systems as important sources of emerging contaminants, raising health concerns since many of these chemicals, once discharged, end up in groundwater and drinking water supplies.
Known as contaminants of emerging concern (CECs), these types of pollutants are frequently detected in U.S. rivers, lakes, and drinking water supplies. However, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency does not currently regulate them in drinking water. Many emerging contaminants are hormone disruptors.
NOAA and international partners plan upgrade of global weather and ocean observing system
NOAA met with ocean observations experts from six nations and 13 global organizations in May 2017 in Honolulu, Hawaii, to plan for the redesign of the Tropical Pacific Observing System by the year 2020 (TPOS 2020).
TPOS is an ocean-based monitoring network comprised of a variety of observing technologies, operated by NOAA and other foreign partners. This network provides the essential ocean data needed to understand important environmental phenomenon and develop weather and climate forecasts for the US and countries around the world.
Biodiversity loss from deep-sea mining will be unavoidable
Biodiversity losses from deep-sea mining are unavoidable and possibly irrevocable, an international team of 15 marine scientists, resource economists and legal scholars argue in a letter published today in the journal Nature Geoscience.
The experts say the International Seabed Authority (ISA), which is responsible under the UN Law of the Sea for regulating undersea mining in areas outside national jurisdictions, must recognize this risk. They say it must also communicate the risk clearly to its member states and the public to inform discussions about whether deep-seabed mining should proceed, and if so, what standards and safeguards need to be put into place to minimize biodiversity loss.
Monitoring changes in wetland extent can help predict the rate of climate change
Monitoring changes to the amount of wetlands in regions where permafrost is thawing should be at the forefront of efforts to predict future rates of climate change, new research shows.
Permafrost - frozen ground - holds huge amounts of carbon which may be released into the atmosphere as the climate warms and these soils thaw. For this reason it is critically important to know where thaw is taking place and how much carbon is being exposed.