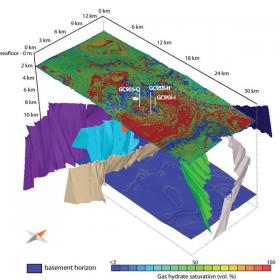
Dr. Ewa Burwicz-Galerne from the GEOMAR Helmholtz Center for Ocean Research Kiel has been awarded during the ninth International Gas Hydrate Conference (ICGH9) in Denver (Colorado, USA) for the world's best PhD thesis in the field of natural gas hydrate research in the past three years. For her thesis, the geologist has developed some of the most complex numerical models of gas hydrates and has gained new insights into their development. The latest study recently was published in the international journal Geochemistry Geophysics, Geosystems.
articles
Seasonality of Sea Ice Enhances Climate Warming in the Arctic
The sea ice cover of the Arctic Ocean shrinks rapidly with most ice loss observed during the summer months. A new study under participation of the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel recently published in the international peer-reviewed journal Scientific Reports shows that this sea ice cover becomes increasingly seasonal. As the authors state the strongest changes in the Arctic can be expected to occur in the coming decade.
Ensuring carpoolers are compatible is key to ridesharing success
Ensuring that would-be carpoolers are riding with people they actually like could potentially decrease car use by nearly 60 per cent, research from a professor at the University of Waterloo has found.
Researchers use virtual reality to unpick causes of common diseases
Researchers from the University of Oxford are using a unique blend of virtual reality and innovative genetic techniques to understand the causes of diseases such as diabetes and anaemia.
York study finds exposure to neonics results in early death for honeybee workers and queens
Worker and queen honeybees exposed to field-realistic levels of neonicotinoid insecticides die sooner, reducing the health of the entire colony, a new study led by York University biologists has found.
Researchers were also surprised to find the neonicotinoid-contaminated pollen collected by the honeybees came not from crops grown from neonicotinoid-treated seeds, but plants growing in areas adjacent to those crops.
Beech trees native to Scotland after all, scientists discover
Beech trees should be considered native to Scotland – despite a long-running debate over their national identity, researchers at the University of Stirling and Science and Advice for Scottish Agriculture (SASA) report.