La agricultura es responsable del 90% de toda la contaminación de amoníaco en Europa, una parte considerable de los cuales proviene del manejo de las deyecciones ganaderas: un nuevo estudio muestra los pasos a seguir para reducir esta contaminación.
articles
From Ancient Fossils to Future Cars
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside’s Bourns College of Engineering have developed an inexpensive, energy-efficient way to create silicon-based anodes for lithium-ion batteries from the fossilized remains of single-celled algae called diatoms. The research could lead to the development of ultra-high capacity lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles and portable electronics.
Protecting people and planet from "invisible killer" is focus of UN health campaign to tackle air pollution
The United Nations World Health Organization (WHO) in partnership with the Coalition for Climate and Clean Air (CCAC) and the Government of Norway has launched a global awareness campaign on the dangers of air pollution – especially ‘invisible killers’ such as black carbon, ground-level ozone and methane – for the health of individuals and the planet.
Titled BreatheLife: Clean air. A healthy future, the campaign aims to mobilize cities and their inhabitants on issues of health and protecting the planet from the effects of air pollution. Moreover, By WHO and CCAC joining forces, ‘BreatheLife’ brings together expertise and partners that can tackle both the climate and health impacts of air pollution.
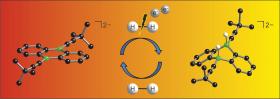
Non-metal catalyst splits hydrogen molecule
Hydrogen (H2) is an extremely simple molecule and yet a valuable raw material which as a result of the development of sophisticated catalysts is becoming more and more important. In industry and commerce, applications range from food and fertilizer manufacture to crude oil cracking to utilization as an energy source in fuel cells. A challenge lies in splitting the strong H-H bond under mild conditions. Chemists at Goethe University have now developed a new catalyst for the activation of hydrogen by introducing boron atoms into a common organic molecule. The process, which was described in theAngewandte Chemie journal, requires only an electron source in addition and should therefore be usable on a broad scale in future.
Scientists find link between tropical storms and decline of river deltas
Research by the University of Southampton shows that a change in the patterns of tropical storms is threatening the future of the Mekong River delta in Vietnam, indicating a similar risk to other deltas around the world.
The study, funded by the UK Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and undertaken in collaboration with the universities of Exeter (UK), Hull (UK), Illinois (USA) and Aalto University (Finland), found that changes in the behaviour of cyclones mean less sediment is running into rivers upstream of the Mekong delta, starving it of material vital for guarding against flooding. The findings are published in the journal Nature.
New perovskite solar cell design could outperform existing commercial technologies, Stanford and Oxford scientists report
A new design for solar cells that uses inexpensive, commonly available materials could rival and even outperform conventional cells made of silicon.
Writing in the Oct. 21 edition of Science, researchers from Stanford and Oxford describe using tin and other abundant elements to create novel forms of perovskite – a photovoltaic crystalline material that’s thinner, more flexible and easier to manufacture than silicon crystals.