New research suggests that the capacity of the terrestrial biosphere to absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) may have been underestimated in past calculations due to certain land-use changes not being fully taken into account.
articles
Scientists explain how meltwater reaches ocean depths
An international team of researchers has discovered why fresh water, melted from Antarctic ice sheets, is often detected below the surface of the ocean, rather than rising to the top above denser seawater. The team found that the Earth’s rotation influences the way meltwater behaves – keeping it at depths of several hundred metres. The research is published this week in the journal Nature in association with colleagues at University of Southampton, National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, University of East Anglia (UEA), British Antarctic Survey (BAS) and Stockholm University.
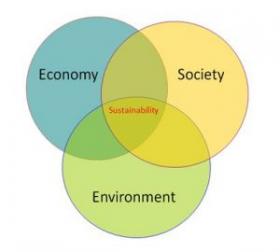
Getting the Measure of Sustainable Economic Growth
The new Index of Sustainable Economic Growth shows there is a shift to strike a healthier balance between support for the economy, and care for essential social and environmental systems. But can it ever replace GDP as a measure of progress?
Unexpected result: Ocean acidification can promote shell formation
Fact: More carbon dioxide (CO2) in the air also acidifies the oceans. It seemed to be the logical conclusion that shellfish and corals will suffer, because chalk formation becomes more difficult in more acidic seawater. But now a group of Dutch and Japanese scientists discovered to their own surprise that some tiny unicellular shellfish make better shells in an acidic environment. This is a completely new insight.
Researchers from the NIOZ (Royal Dutch Institute for Sea Research) and JAMSTEC (Japanese Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology) found in their experiments that so-called foraminifera might even make their shells better in more acidic water. These single-celled foraminifera shellfish occur in huge numbers in the oceans. The results of the study are published in the leading scientific journal ‘Nature Communications’.
Study: How Climate Change Threatens Mountaintops (and Clean Water)
Mountains are far more than rocks. They also confer various natural benefits—for example, about half of the world’s drinking water filters through their high-elevation forests, plants, and soils.
Now, a new, first-of-its kind study, in the journal Nature, shows how these mountain ecosystems around the globe may be threatened by climate change.
Rising temperatures over the next decades appear likely to “decouple” key nutrient cycles in mountain soils and plants, an international team of sixteen scientists reports. Their study suggests that this is expected to disrupt the function of mountaintop ecosystems, as plant communities above and at treeline are thrown into turmoil faster than trees can migrate uphill in a warmer world.
DNA analysis of seawater detects 80% of fish species in just one day
A Japanese research group has used a new technology that identifies multiple fish species populating local areas by analyzing DNA samples from seawater, and proved that this method is accurate and more effective than visual observation.
This research was carried out as part of the Japan Science and Technology Strategic Basic Research Programs by a group including Academic Researcher YAMAMOTO Satoshi (Kobe University Graduate School of Human Development and Environment), Associate Professor MASUDA Reiji (Kyoto University), Professor ARAKI Hitoshi (Hokkaido University), Professor KONDOH Michio (Ryukoku University), Project Assistant Professor MINAMOTO Toshifumi (Kobe University Graduate School of Human Development and Environment), and Adjunct Associate Professor MIYA Masaki (Head of Department of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, Natural History Museum and Institute, Chiba).