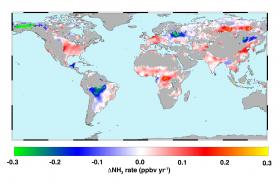
The first global, long-term satellite study of airborne ammonia gas has revealed “hotspots” of the pollutant over four of the world’s most productive agricultural regions. The results of the study, conducted using data from NASA’s Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument on NASA’s Aqua satellite, could inform the development of strategies to control pollution from ammonia and ammonia byproducts in Earth’s agricultural areas.
A University of Maryland-led team discovered steadily increasing ammonia concentrations from 2002 to 2016 over agricultural centers in the United States, Europe, China and India. Increased concentrations of atmospheric ammonia are linked to poor air and water quality.