Many people choose organic thinking it’s better for humans and the planet, but a new UBC study published today in Science Advances finds that might not always be the case.
articles
Mayo Clinic discovers high-intensity aerobic training can reverse aging processes in adults
Everyone knows that exercise is good for you, but what type of training helps most, especially when you’re older - say over 65? A Mayo Clinic study says it’s high-intensity aerobic exercise, which can reverse some cellular aspects of aging. The findings appear in Cell Metabolism.
Mayo researchers compared high-intensity interval training, resistance training and combined training. All training types improved lean body mass and insulin sensitivity, but only high-intensity and combined training improved aerobic capacity and mitochondrial function for skeletal muscle. Decline in mitochondrial content and function are common in older adults.
Fukushima catastrophe unfolds ... key facts and figures for an unhappy sixth anniversary
The 2011 Fukushima catastrophe is an ongoing disaster whose end only gets more remote as time passes. The government is desperate to get evacuees back into their homes for the 2020 Tokyo Olympics, but the problems on the ground, and in the breached reactor vessels, are only getting more serious and costly, as unbelievable volumes of radiation contaminate land, air and ocean.
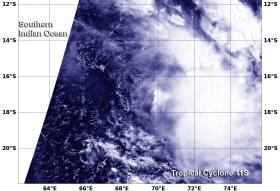
NASA Sees Wind Shear Affecting Tropical Cyclone 11S
Tropical Cyclone 11S appeared elongated in NASA satellite imagery as a result of the storm being battered by wind shear.
When NASA's Terra satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone 11S on March 10 at 0515 UTC (12:15 a.m. EST) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument took a visible light picture of the storm. The image revealed that the storm has been stretched out by moderate vertical wind shear.
Measurements by school pupils paved way for key research findings
With their measurements and samples, nearly 3,500 schoolchildren have assisted a research study on lakes and global warming, now published in an academic journal. The results show that water temperatures generally remain low despite the air becoming warmer. This helps to curb the outflow of greenhouse gases.
Volcano Breath: Measuring Sulfur Dioxide from Space
There is no mint that can take the edge off sulfurous emissions from volcanoes, but researchers can use remote sensing to better understand volcanic breathing.
Volcanoes erupt, they spew ash, their scarred flanks sometimes run with both lava and landslides. But only occasionally. A less dramatic but important process is continuous gas emissions from volcanoes; in other words, as they exhale. A number of volcanoes around the world continuously exhale water vapor laced with heavy metals, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide, among many other gases. Of these, sulfur dioxide is the easiest to detect from space.