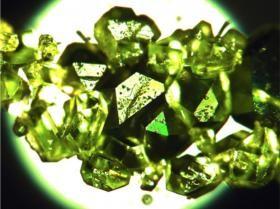
Uno de los nuevos materiales más excitante es una clase de sólidos porosos conocidos como Marcos Metal/Orgánicos, o MOF (por sus siglas en inglés). Estos materiales artificiales se introdujeron en la década de 1990, y los investigadores de todo el mundo están trabajando en maneras de utilizarlos a manera de esponjas moleculares para aplicaciones tales como el almacenamiento de hidrógeno, la captura de carbono o la energía fotovoltaica.
articles
Melting ice sheet could expose frozen Cold War-era hazardous waste
Climate change is threatening to expose hazardous waste at an abandoned camp thought to be buried forever in the Greenland Ice Sheet, new research out of York University has found.
Camp Century, a United States military base built within the Greenland ice sheet in 1959, doubled as a top-secret site for testing the feasibility of deploying nuclear missiles from the Arctic during the Cold War. When the camp was decommissioned in 1967, its infrastructure and waste were abandoned under the assumption they would be entombed forever by perpetual snowfall.
Drought conditions slow the growth of Douglas fir trees across the West
Whether growing along the rim of the Grand Canyon or living in the mist with California's coastal redwoods, Douglas fir trees are consistently sensitive to drought conditions that occur throughout the species' range in the United States, according to a study led by a researcher at the University of California, Davis.
The study, published Aug. 8 in the journalProceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, provides direct evidence of the negative impact of water stress on forest ecosystems. It also pinpointed which conditions are causing low growth among Douglas fir trees.
Undergraduates uncover mechanism tied to plant height
Dwarfed plants add color and a diversity of architectures to landscapes and gardens, and a Purdue University undergraduate class discovered a key mechanism that leads to their small stature. Graduate student Norman Best led an undergraduate plant physiology class in an exercise that identified a mutation in a dwarf variety of sunflower, called Sunspot, that keeps the plant short. The eight Purdue students, along with scientists that supported the work, published their results in the Journal of the American Society of Horticultural Science.
Lake Tanganyika fisheries declining from global warming
The decrease in fishery productivity in Lake Tanganyika since the 1950s is a consequence of global warming rather than just overfishing, according to a new report from an international team led by a University of Arizona geoscientist.
The lake was becoming warmer at the same time in the 1800s the abundance of fish began declining, the team found. The lake's algae - fish food - also started decreasing at that time.
A Troubling Snag in the Comeback of the California Condor
IN THE EARLY ’80s, the California condor almost scavenged its way to extinction. The grisly-looking birds survive off the remains of animals, often leftovers shot by hunters. But those hunters often used lead ammunition. Condors were dying of lead poisoning, their numbers dropping as low as 22.
In one of conservation’s greatest success stories, a frantic captive breeding program brought the huge, glorious scavenger roaring back; today, the condors number close to 450, over half of which are wild. While an outright ban on lead ammunition won’t kick in until 2019, aggressive public education has helped safeguard the species—inland at least. But scientists have found a new threat to the reestablished condors: extremely high levels of mercury and the pesticide DDT in the birds’ blood. This time, it’s an appetite for marine mammal flesh that may threaten the condor.