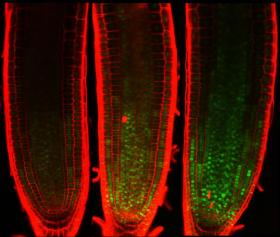
The cell cycle is the system through which a cell grows and divides. It is also how a cell passes its DNA to its progeny and is why the cell cycle ceases if the DNA is damaged, as otherwise it risks passing this damage to daughter cells. Scientists at the Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have reported a new molecular mechanism that explains how this cessation occurs. The study, which can be read in Nature Communications, shows the transcription factor family MYB3R prevents progression to the division stage (M phase) of the cell cycle in Arabidopsis, a small flowering plant that is a member of the mustard family.
articles
New Study Analyses Volcanic Fatalities in More Detail Than Ever Before
It is hoped the findings, published recently in the Journal of Applied Volcanology, will help increase our understanding of volcanic hazards and the subsequent threat to life.
Planning for the Future
Over the past decade, increasing temperatures across much of Africa and decreasing rainfall across East Africa have come to represent an alarming climate trend. Chief among concerns is the impact such conditions have on human health.
Ammonia Emissions Unlikely To Be Causing Extreme China Haze
As China struggles to find ways to remedy the noxious haze that lingers over Beijing and other cities in the winter, researchers from Georgia Institute of Technology have cast serious doubt on one proposed cause: high levels of ammonia in the air.
The wintertime air pollution has gained attention in the scientific community in recent years, prompting some scientists to propose that ammonia, emitted into the air from agricultural activities and automobiles, could be a precursor that strongly promotes the formation of the haze.
Georgia Tech researchers countered that theory in a study published September 21 in the journal Scientific Reports. The study was sponsored by the National Science Foundation.
Sunlight and the right microbes convert Arctic carbon into carbon dioxide
Nearly half of the organic carbon stored in soil around the world is contained in Arctic permafrost, which has experienced rapid melting, and that organic material could be converted to greenhouse gases that would exacerbate global warming.
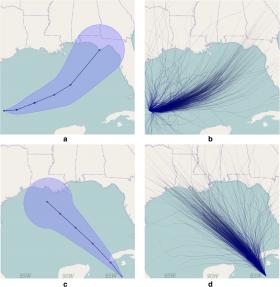
Interpreting Hurricane Forecast Displays Can Be Difficult for General Public
The 2017 hurricane season has highlighted the critical need to communicate a storm’s impact path and intensity accurately, but new research from the University of Utah shows significant misunderstandings of the two most commonly used storm forecast visualization methods.