The cell cycle is the system through which a cell grows and divides. It is also how a cell passes its DNA to its progeny and is why the cell cycle ceases if the DNA is damaged, as otherwise it risks passing this damage to daughter cells. Scientists at the Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have reported a new molecular mechanism that explains how this cessation occurs. The study, which can be read in Nature Communications, shows the transcription factor family MYB3R prevents progression to the division stage (M phase) of the cell cycle in Arabidopsis, a small flowering plant that is a member of the mustard family.
The cell cycle is the system through which a cell grows and divides. It is also how a cell passes its DNA to its progeny and is why the cell cycle ceases if the DNA is damaged, as otherwise it risks passing this damage to daughter cells. Scientists at the Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) have reported a new molecular mechanism that explains how this cessation occurs. The study, which can be read in Nature Communications, shows the transcription factor family MYB3R prevents progression to the division stage (M phase) of the cell cycle in Arabidopsis, a small flowering plant that is a member of the mustard family.
"Inhibition of cell division in response to DNA damage enables cells to maintain genome integrity. The inhibition is regulated by different molecules in animals and plants," explains NAIST Professor Masaaki Umeda, who studies the role of stem cells in plant growth.
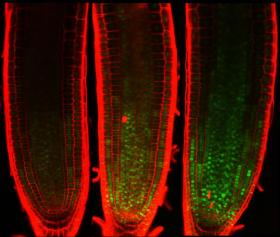
MYB3R can be divided into groups of transcription activators (Act-MYB) and transcription repressors (Rep-MYB). Plants grow through their root tip and shoot apex, but not upon DNA damage. In the study, Prof. Umeda and his colleagues found termination of the growth was accompanied by an accumulation of Rep-MYB proteins in these regions and that absent this accumulation, the plants would show signs of growing leaves and flowers.
Read more at Nara Institute of Science and Technology
Image: Green spots indicate a transcription factor that accumulates and inhibits cell division upon DNA damage. Researchers found an indispensable role of the transcription factor in arresting plant growth under stressful conditions. (Credit: Masaaki Umeda)