Researchers have found that the formation and breakup of supercontinents over hundreds of millions of years controls volcanic carbon emissions. The results, reported in the journal Science, could lead to a reinterpretation of how the carbon cycle has evolved over Earth’s history, and how this has impacted the evolution of Earth’s habitability.
articles
Sparkling springs aid quest for underground heat
Analysis of natural sparkling mineral water has given scientists valuable clues on how to locate hot water springs.
Cost of diabetes care in Africa could triple by 2030
The costs and complications of diabetes could overwhelm healthcare systems in Sub-Saharan Africa and reach US$59.3 billion by 2030 if rates double, according to the Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology Commission.
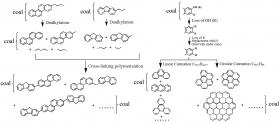
Scientists Uncover Biogeochemical Controls on Occurrence and Distribution of PACs in Coals
The organic matter in coal contains polycyclic aromatic compounds (PACs) of varying quantities in diverse soluble and insoluble forms. PACs in coal are of special interest for organic geochemical studies as they have been successfully used as biological marker compounds (biomarkers) and indicators of thermal maturity.
However, challenges exist when applying PACs in understanding the organic geochemistry of coal. For example, what are the sources of PACs in coals? How do they transform during the long-term coal-formation history? Is there any regular relationship between the PAC and macro-molecular structural changes?
Holographic Imaging Could Be Used to Detect Signs of Life in Space
We may be capable of finding microbes in space—but if we did, could we tell what they were, and that they were alive?
To Shrink The Mosquito Population, Scientists Are Releasing 20 Million Of Them
This summer, scientists in California are releasing 20 million mosquitoes in an effort to shrink the population of mosquitoes that can carry diseases.