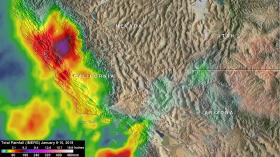
Winter rains falling on recently burned ground triggered deadly mudslides in Santa Barbara County, California on January 9. NASA calculated the amount of rain fall between January 8 and 10, 2018 and calculated the potential for landslides.
articles
Please Do Not Assault the Towering Robot That Roams Walmart
If you think shopping is tedious, try juggling 200,000 products in a Walmart. Not literally, of course, but somehow keeping the shelves stocked over an area of tens of thousands of square feet. For that you need a worker with a barcode scanner and an enviable amount of patience.
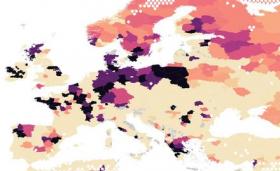
Adaptation now: River flood risks increase around the globe under future warming
Rainfall changes caused by global warming will increase river flood risks across the globe. Already today, fluvial floods are among the most common and devastating natural disasters.
3-D Structure of Buried Ice Sheets on Mars Revealed by High-Resolution Images
For the first time, high-resolution images show the three-dimensional structure of massive ice deposits on Mars. According to an in-depth analysis led by the USGS, the images reveal never-before-observed details about the ice sheets, including that some begin just a few feet below the Martian surface and extend to depths greater than 300 feet.
Rising temperatures turning major sea turtle population female
Scientists have used a new research approach to show that warming temperatures are turning one of the world’s largest sea turtle colonies almost entirely female, running the risk that the colony cannot sustain itself in coming decades, newly published research concludes.
Airing dirty laundry: Students develop new way to measure plastics released in environment while washing clothes
Two undergraduate students researching pollution have helped develop a new way to measure how much plastic is released into the environment from laundering clothes – which may be contributing to plastic pollution choking the world's oceans.