Proxima Centauri is the closest star to the Sun. It is a faint red dwarf lying just four light-years away in the southern constellation of Centaurus (The Centaur). It is orbited by the Earth-sized temperate world Proxima b, discovered in 2016 and the closest planet to the Solar System. But there is more to this system than just a single planet. The new ALMA observations reveal emission from clouds of cold cosmic dust surrounding the star.
articles
Protecting the Wild: Baylor Professor Helps to Minimize Recreation Disturbance to Wildlife
Nature and outdoor enthusiasts seek to enjoy recreational activities such as hiking, mountain biking, horseback riding and camping. However, sometimes appreciating nature’s beauty comes at a cost to wildlife.
Professor Provides Fisheries a Solution to Overharvesting
There are fewer fish in the sea – literally.
Consumer demand and inadequate scientific information has led to overharvesting, reducing fish species and fish stocks around the world.
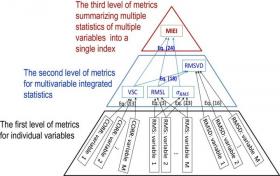
A New Method to Evaluate Overall Performance of a Climate Model in Simulating Multiple Fields
Many climate-related studies, such as detection and attribution of historical climate change, projections of future climate and environments, and adaptation to future climate change, heavily rely on the performance of climate models. Concisely summarizing and evaluating model performance becomes increasingly important for climate model intercomparison and application, especially when more and more climate models participate in international model intercomparison projects.
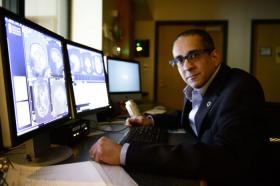
Post-concussion brain changes persist even after pre-teen hockey players return to play
Young hockey players who have suffered concussions may still show changes in the white matter of the brain months after being cleared to return to play, researchers at Western University have found through sophisticated Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) techniques.
Urban-Based Evolution: Species Are Rapidly Adapting to City Habitats
Cities around the globe are fueling evolution among microbes, plants, and animals, driving physical mutations and altering gene flow, according to a new analysis in the journal Science. The projected spread of urbanization in coming decades will continue to reshape and create new species in unexpected ways, the study found.