Operated by NASA and the French space agency, the Surface Water and Ocean Topography mission provides a new view of water on land, at the coast, and in the ocean.
Operated by NASA and the French space agency, the Surface Water and Ocean Topography mission provides a new view of water on land, at the coast, and in the ocean.
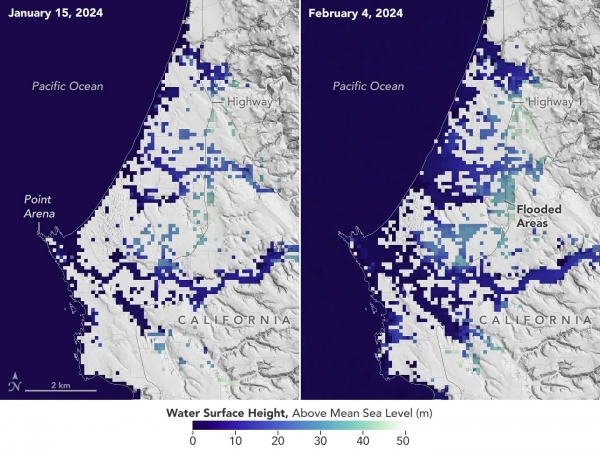
A series of atmospheric rivers drenched California in February, with record amounts of rainfall and hurricane-force winds sweeping across parts of the state. At one point, weather agencies posted flood watches for nearly the entirety of California’s coast. The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission captured data on some of the flooding near the community of Manchester, roughly 105 miles (169 kilometers) north of San Francisco. The satellite is a collaboration between NASA and the French space agency, CNES (Centre National d’Études Spatiales).
The image above shows the area on Jan. 15, before the rain and snow from atmospheric rivers, and then again on Feb. 4, after the first in a series of storms soaked California. Water heights are shown in shades of green and blue, with lighter hues indicating the highest levels relative to mean sea level. (Data for inland areas includes the height of the floodwaters plus the ground elevation beneath it.) Some coastal areas were flooded by both ocean tides and heavy rain, while others were likely flooded only by precipitation. Each pixel in the image represents an area that is 330 feet by 330 feet (100 meters by 100 meters).
Read more at NASA
Image: This image shows SWOT satellite data for water surface height in part of Mendocino County, Northern California, on Jan. 15, before several atmospheric rivers arrived, and on Feb. 4, after the first storms. Light blue and green indicate the highest water levels relative to mean sea level. (Inland water heights include the underlying ground elevation.)
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech