Climate change has threatened the global environment and biodiversity, particularly the aquatic ecosystems as well as the development of human ecosociety. The Tibetan Plateau is the region possessing the richest water resources in Asia but highly affected by the global climate change.
Climate change has threatened the global environment and biodiversity, particularly the aquatic ecosystems as well as the development of human ecosociety. The Tibetan Plateau is the region possessing the richest water resources in Asia but highly affected by the global climate change.
The intensified water cycling has increasingly affected aquatic environment since the 1980s. Glacial retreat, permafrost degradation, and changes in the precipitation regime resulted in a general lake expansion and river discharge changes across the whole region. However, it is largely unknown how aquatic ecosystems here respond to climate change.
The Research Group of Biological Invasion and Adaptive Evolution (BIAE; PI: CHEN Yifeng) at Institute of Hydrobiology (IHB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently answered how reproductive phenology of Gymnocypris selincuoensis, an endemic fish in Lake Selicuo in Tibetan Plateau, associated with climate changes.
Results showed that the reproductive phenology of G. selincuoensis was strongly advanced during the 1970s and 2000s. Growing season of G. selincuoensis has been increased by 17 days at a rate of three days per decade on average.
Read more at Chinese Academy of Sciences Headquarters
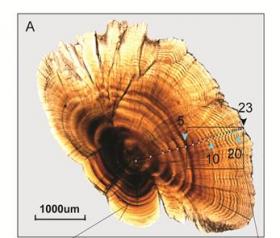
Image: This is sectioned otolith of G. selincuoensis. (Credit: CHEN Yifeng)