Recording electrical signals from inside a neuron in the living brain can reveal a great deal of information about that neuron’s function and how it coordinates with other cells in the brain. However, performing this kind of recording is extremely difficult, so only a handful of neuroscience labs around the world do it.
To make this technique more widely available, MIT engineers have now devised a way to automate the process, using a computer algorithm that analyzes microscope images and guides a robotic arm to the target cell.
Recording electrical signals from inside a neuron in the living brain can reveal a great deal of information about that neuron’s function and how it coordinates with other cells in the brain. However, performing this kind of recording is extremely difficult, so only a handful of neuroscience labs around the world do it.
To make this technique more widely available, MIT engineers have now devised a way to automate the process, using a computer algorithm that analyzes microscope images and guides a robotic arm to the target cell.
This technology could allow more scientists to study single neurons and learn how they interact with other cells to enable cognition, sensory perception, and other brain functions. Researchers could also use it to learn more about how neural circuits are affected by brain disorders.
“Knowing how neurons communicate is fundamental to basic and clinical neuroscience. Our hope is this technology will allow you to look at what’s happening inside a cell, in terms of neural computation, or in a disease state,” says Ed Boyden, an associate professor of biological engineering and brain and cognitive sciences at MIT, and a member of MIT’s Media Lab and McGovern Institute for Brain Research.
Continue reading at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
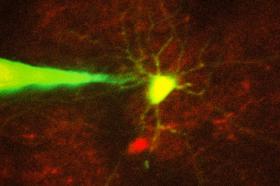
Image: MIT engineers have devised a way to automate the process of monitoring neurons in a living brain using a computer algorithm that analyzes microscope images and guides a robotic arm to the target cell. In this image, a pipette guided by a robotic arm approaches a neuron identified with a fluorescent stain. Credit: Ho-Jun Suk