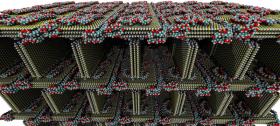
Rice University materials scientists have created a light foam from two-dimensional sheets of hexagonal-boron nitride (h-BN) that absorbs carbon dioxide.
They discovered freeze-drying h-BN turned it into a macro-scale foam that disintegrates in liquids. But adding a bit of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) into the mix transformed it into a far more robust and useful material.
The foam is highly porous and its properties can be tuned for use in air filters and as gas absorption materials, according to researchers in the Rice lab of materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan.
Their work appears in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano.
Rice University materials scientists have created a light foam from two-dimensional sheets of hexagonal-boron nitride (h-BN) that absorbs carbon dioxide.
They discovered freeze-drying h-BN turned it into a macro-scale foam that disintegrates in liquids. But adding a bit of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) into the mix transformed it into a far more robust and useful material.
The foam is highly porous and its properties can be tuned for use in air filters and as gas absorption materials, according to researchers in the Rice lab of materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan.
Their work appears in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Nano.
The polyvinyl alcohol serves as a glue. Mixed into a solution with flakes of h-BN, it binds the junctions as the microscopic sheets arrange themselves into a lattice when freeze-dried. The one-step process is scalable, the researchers said.
Read more at Rice University
Image: A molecular dynamics simulation shows polyvinyl alcohol molecules of carbon (teal), oxygen (red) and hydrogen (white) binding two-dimensional sheets of hexagonal-boron nitride (blue and yellow). The reusable material created at Rice University can sequester more than three times its weight in carbon dioxide. Courtesy of the Ajayan Research Group