Chemists have figured out a new, more efficient way to create carbon-based fuels from carbon dioxide (CO2). In chemical reactions performed in the lab, a Caltech team has identified a new additive that helps selectively convert CO2 into fuels containing multiple carbon atoms—a step toward ultimately making renewable liquid fuels that are not derived from coal or oil.
"The results were quite shocking," says Jonas Peters, Bren Professor of Chemistry at Caltech and director of the Resnick Sustainability Institute, who jointly led the research in collaboration with Theodor Agapie, professor of chemistry at Caltech. "Usually, in these types of reactions with CO2, you see a lot of by-products like methane and hydrogen. In this case, the reaction was highly selective for the more desirable fuels that contain multiple carbons—such as ethylene, ethanol, and propanol. We saw an 80 percent conversion to these multi-carbon fuel products, with only 20 percent or so going into hydrogen and methane."
Chemists have figured out a new, more efficient way to create carbon-based fuels from carbon dioxide (CO2). In chemical reactions performed in the lab, a Caltech team has identified a new additive that helps selectively convert CO2 into fuels containing multiple carbon atoms—a step toward ultimately making renewable liquid fuels that are not derived from coal or oil.
"The results were quite shocking," says Jonas Peters, Bren Professor of Chemistry at Caltech and director of the Resnick Sustainability Institute, who jointly led the research in collaboration with Theodor Agapie, professor of chemistry at Caltech. "Usually, in these types of reactions with CO2, you see a lot of by-products like methane and hydrogen. In this case, the reaction was highly selective for the more desirable fuels that contain multiple carbons—such as ethylene, ethanol, and propanol. We saw an 80 percent conversion to these multi-carbon fuel products, with only 20 percent or so going into hydrogen and methane."
Fuels with multiple carbon atoms are more desirable because they tend to be liquid—and liquid fuels store more energy per volume than gaseous ones. For instance, propanol, which is liquid and contains three carbon atoms, stores more energy than methane, which is a gas and only has one carbon atom.
Read more at California Institute of Technology
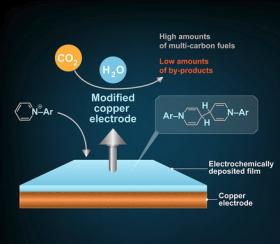
Image: This diagram illustrates the process by which Caltech researchers converted carbon dioxide (CO2) into fuel products containing multiple carbon atoms (fuels with multiple carbons tend to be liquids and liquid fuels store more energy per volume than gas ones). They used an additive called N-substituted arylpyridiniums in their chemical reactions, which deposited a thin film on a copper electrode. The film helped more selectively convert CO2 into the desired fuels.
Credit: Caltech