Lamprey are slimy, parasitic eel-like fish, one of only two existing species of vertebrates that have no jaw. While many would be repulsed by these creatures, lamprey are exciting to biologists because they are so primitive, retaining many characteristics similar to their ancient ancestors and thus offering answers to some of life's biggest evolutionary questions. Now, by studying the lamprey, Caltech researchers have discovered an unexpected mechanism for the evolution of the neurons of the peripheral nervous system—nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Lamprey are slimy, parasitic eel-like fish, one of only two existing species of vertebrates that have no jaw. While many would be repulsed by these creatures, lamprey are exciting to biologists because they are so primitive, retaining many characteristics similar to their ancient ancestors and thus offering answers to some of life's biggest evolutionary questions. Now, by studying the lamprey, Caltech researchers have discovered an unexpected mechanism for the evolution of the neurons of the peripheral nervous system—nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord.
The work was done in the laboratory of Marianne Bronner, the Albert Billings Ruddock Professor of Biology at Caltech, and appears in a paper in the March 20 online issue of Nature.
For over a decade, the Bronner group has studied lamprey because of the unique insights they offer into the evolution of vertebrates, and particularly the evolution of new structures like jaws. Her laboratory at Caltech maintains one of the very few laboratory populations of lamprey in the world.
Read more at California Institute of Technology
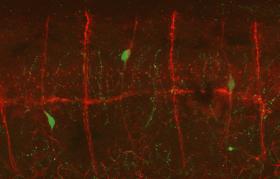
Image: Embryonic nerve cells (green) journey across spinal nerves (red) to reach the gut. These neural precursor cells will develop into neurons when they reach the gut. (Credit: Courtesy of the Bronner laboratory)