More efficient sensors are needed to be able to detect environmental pollution. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have proposed a new, sophisticated method of detecting molecules with sensors based on ultra-thin nanomaterials. The novel method could improve environmental sensing in the future. The results are published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
“This could open up new possibilities for the detection of environmental gases. Our method is more robust than conventional sensors, which rely on small changes in optical properties”, says Maja Feierabend, PhD student at the Department of Physics and the main author of the article from Chalmers University of Technology and Technische Universität Berlin.
More efficient sensors are needed to be able to detect environmental pollution. Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology have proposed a new, sophisticated method of detecting molecules with sensors based on ultra-thin nanomaterials. The novel method could improve environmental sensing in the future. The results are published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.
“This could open up new possibilities for the detection of environmental gases. Our method is more robust than conventional sensors, which rely on small changes in optical properties”, says Maja Feierabend, PhD student at the Department of Physics and the main author of the article from Chalmers University of Technology and Technische Universität Berlin.
Together with her supervisor, Associate Professor Ermin Malic, and Gunnar Berghäuser, postdoctoral researcher at Chalmers, she has proposed a new type of chemical nanosensor that consists of atomically thin nanomaterials that are extremely sensitive to changes in their surroundings.
Continue reading at Chalmers University of Technology
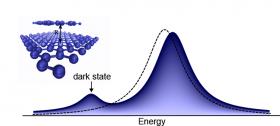
Caption: Molecules are identified by activating dark electronic states in the sensor material, resulting in a new visible peak. The altered optical fingerprint of the material proves the presence of molecules.
Credit: Maja Feierabend and Ermin Malic (License: CC 3.0)