A small subset of the most intense droughts move across continents in predictable patterns, according a new study published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters by researchers in Austria and the United States. The study could help improve projections of future drought, allowing for more effective planning.
A small subset of the most intense droughts move across continents in predictable patterns, according a new study published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters by researchers in Austria and the United States. The study could help improve projections of future drought, allowing for more effective planning.
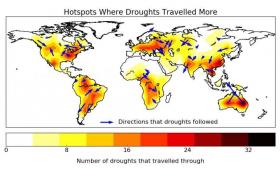
While most droughts tend to stay put near where they started, approximately 10% travel between 1,400 to 3,100 kilometers (depending on the continent), the study found. These traveling droughts also tend to be the largest and most severe ones, with the highest potential for damage to the agriculture, energy, water, and humanitarian aid sectors.
“Most people think of a drought as a local or regional problem, but some intense droughts actually migrate, like a slow-motion hurricane on a timescale of months to years instead of days to weeks," says Julio Herrera-Estrada, a graduate student in civil and environmental engineering at Princeton, who led the study.
Read more at International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis
Image: Drought hotspots and movement directions identified in the new study. (Credit: Herrera-Estrada et al 2017)