Last year will go down in history as the year when the planet’s atmosphere broke a startling record: 400 parts per million of carbon dioxide. The last time the planet’s air was so rich in CO2 was millions of years ago, back before early predecessors to humans were likely wielding stone tools; the world was a few degrees hotter back then, and melted ice put sea levels tens of meters higher.
“We’re in a new era,” says Ralph Keeling, director of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography’s CO2 Program in San Diego. “And it’s going fast. We’re going to touch up against 410 pretty soon.”
Last year will go down in history as the year when the planet’s atmosphere broke a startling record: 400 parts per million of carbon dioxide. The last time the planet’s air was so rich in CO2 was millions of years ago, back before early predecessors to humans were likely wielding stone tools; the world was a few degrees hotter back then, and melted ice put sea levels tens of meters higher.
“We’re in a new era,” says Ralph Keeling, director of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography’s CO2 Program in San Diego. “And it’s going fast. We’re going to touch up against 410 pretty soon.”
There’s nothing particularly magic about the number 400. But for environmental scientists and advocates grappling with the invisible, intangible threat of rising carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, this symbolic target has served as a clear red line into a danger zone of climate change.
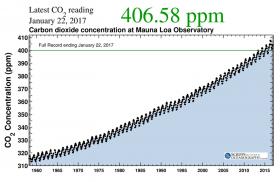
When scientists (specifically, Ralph Keeling’s father) first started measuring atmospheric CO2 consistently in 1958, at the pristine Mauna Loa mountaintop observatory in Hawaii, the CO2 level stood at 316 parts per million (ppm), just a little higher than the pre-industrial level of 280 ppm. 400 was simply the next big, round number looming in our future.
Continue reading at Yale Environment 360
Image: Concentrations of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere have risen rapidly since measurements began nearly 60 years ago, climbing from 316 parts per million (ppm) in 1958 to more than 400 ppm today
Credit: Scripps Institution of Oceanography