The first molecular study of an organism able to survive intracellular freezing (freezing within its cells) is published this week by British Antarctic Survey (BAS), in collaboration with researchers from the University of Otago, New Zealand. The paper represents a milestone in scientists’ understanding of an extraordinary adaptation.
The first molecular study of an organism able to survive intracellular freezing (freezing within its cells) is published this week by British Antarctic Survey (BAS), in collaboration with researchers from the University of Otago, New Zealand. The paper represents a milestone in scientists’ understanding of an extraordinary adaptation.
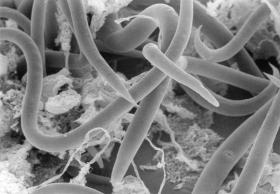
The tiny Antarctic nematode, more commonly known as a round worm, (Panagrolaimus sp. DAW1) was cultured from a coastal Antarctic penguin rookery at McMurdo Sound, and is the best-documented organism able to survive the disruptions brought about by total freezing. The nematode is also able to undergo a form of freeze avoidance by eliminating all of its water content, called cryoprotective dehydration. However, it is the ability to survive intracellular freezing which makes this organism really stand out.
Exploring gene expression patterns, the researchers were able to show how molecularly active the nematodes are while in a frozen state, highlighting certain key genes enabling them to endure such an extreme physical state.
This is the first study of its kind, shedding light on a possibly rare adaptation, which could lead to new applications.
Read more at British Artarctic Survey
Photo: Antarctic nematode worms photographed under the microscope – credit: David Wharton