Scientists have evidence that Popeye was right: Spinach makes you stronger. But it’s the high nitrate content in the leafy greens — not the iron — that creates the effect.
Building on a growing body of work that suggests dietary nitrate improves muscle performance in many elite athletes, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis found that drinking concentrated beet juice — also high in nitrates — increases muscle power in patients with heart failure.
“It’s a small study, but we see robust changes in muscle power about two hours after patients drink the beet juice,” said senior author Linda R. Peterson, MD, associate professor of medicine. “A lot of the activities of daily living are power-based — getting out of a chair, lifting groceries, climbing stairs. And they have a major impact on quality of life. We want to help make people more powerful because power is such an important predictor of how well people do, whether they have heart failure, cancer or other conditions. In general, physically more powerful people live longer.”
Scientists have evidence that Popeye was right: Spinach makes you stronger. But it’s the high nitrate content in the leafy greens — not the iron — that creates the effect.
Building on a growing body of work that suggests dietary nitrate improves muscle performance in many elite athletes, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis found that drinking concentrated beet juice — also high in nitrates — increases muscle power in patients with heart failure.
“It’s a small study, but we see robust changes in muscle power about two hours after patients drink the beet juice,” said senior author Linda R. Peterson, MD, associate professor of medicine. “A lot of the activities of daily living are power-based — getting out of a chair, lifting groceries, climbing stairs. And they have a major impact on quality of life. We want to help make people more powerful because power is such an important predictor of how well people do, whether they have heart failure, cancer or other conditions. In general, physically more powerful people live longer.”
Based on research in elite athletes, especially cyclists who use beet juice to boost performance, the study’s corresponding author, Andrew R. Coggan​, PhD, assistant professor of radiology, suggested trying the same strategy in patients with heart failure.​​​​​​​​​​​​​
In the September issue of the journal Circulation: Heart Failure, the scientists reported data from nine patients with heart failure. Two hours after the treatment, patients demonstrated a 13 percent increase in power in muscles that extend the knee. The researchers observed the most substantial benefit when the muscles moved at the highest velocities. The increase in muscle performance was significant in quick, power-based actions, but researchers saw no improvements in performance during longer tests that measure muscle fatigue.
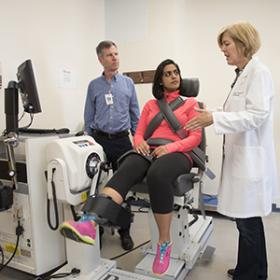
Cardiology fellow Nishtha Sodhi, MD, (center) demonstrates equipment used to measure muscle power. A study co-authored by Andrew Coggan, PhD, (left) and Linda Peterson, MD, showed that drinking concentrated beet juice boosts muscle power in patients with heart failure. Image credit ROBERT BOSTON.
Read more at Washington University School of Medicine.