When it comes to skin infections, a healthy and robust immune response may depend greatly upon what lies beneath. In a new paper published in the January 2, 2015 issue of Science, researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine report the surprising discovery that fat cells below the skin help protect us from bacteria.
Richard Gallo, MD, PhD, professor and chief of dermatology at UC San Diego School of Medicine, and colleagues have uncovered a previously unknown role for dermal fat cells, known as adipocytes: They produce antimicrobial peptides that help fend off invading bacteria and other pathogens.
When it comes to skin infections, a healthy and robust immune response may depend greatly upon what lies beneath. In a new paper published in the January 2, 2015 issue of Science, researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine report the surprising discovery that fat cells below the skin help protect us from bacteria.
Richard Gallo, MD, PhD, professor and chief of dermatology at UC San Diego School of Medicine, and colleagues have uncovered a previously unknown role for dermal fat cells, known as adipocytes: They produce antimicrobial peptides that help fend off invading bacteria and other pathogens.
"It was thought that once the skin barrier was broken, it was entirely the responsibility of circulating (white) blood cells like neutrophils and macrophages to protect us from getting sepsis," said Gallo, the study's principal investigator.
"But it takes time to recruit these cells (to the wound site). We now show that the fat stem cells are responsible for protecting us. That was totally unexpected. It was not known that adipocytes could produce antimicrobials, let alone that they make almost as much as a neutrophil."
The human body's defense against microbial infection is complex, multi-tiered and involves numerous cell types, culminating in the arrival of neutrophils and monocytes - specialized cells that literally devour targeted pathogens.
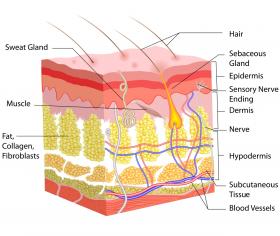
Skin graphic image via Shutterstock.
Read more at EurekAlert.