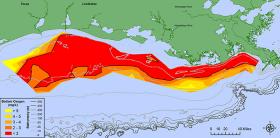
Scientists have determined this year’s Gulf of Mexico “dead zone,” an area of low oxygen that can kill fish and marine life, is 8,776 square miles, an area about the size of New Jersey. It is the largest measured since dead zone mapping began there in 1985.
The measured size is close to the 8,185 square miles forecast by NOAA in June.