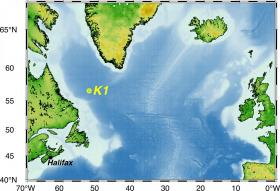
The Labrador Sea in the North Atlantic is one of the few areas in the world ocean where cold, saline seawater sinks to large depths and forms deep water. This convection process also transports oxygen into the deep sea. A team of scientists from Scripps Institution of Oceanography (San Diego, California), Dalhousie University (Halifax, Canada) and GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel have now published the analysis of data obtained from the mooring K1 in the international scientific journal Geophysical Research Letters. The results show that in winter 2014/2015 an unusually high amount of oxygen was absorbed by the ocean in the region. The actual oxygen uptake at the sea surface is very difficult to determine directly, but the scientists were able to derive the oxygen uptake from the oxygen content measured throughout the water column. One of the questions the scientists were concerned with: Can the strong oxygen uptake in the Labrador Sea compensate the global oxygen loss of the ocean?
articles
Diverse Landscapes Are More Productive and Adapt better to Climate Change
The dramatic, worldwide loss of biodiversity is one of today's greatest environmental problems. The loss of species diversity affects important ecosystems on which humans depend. Previous research predominantly addressed short-term effects of biodiversity in small experimental plots planted with few randomly selected plant species. These studies have shown that species-poor plant assemblages function less well and produce less biomass than species rich systems.
A revolution in lithium-ion batteries is becoming more realistic
The modern world relies on portable electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, cameras or camcorders. Many of these devices are powered by lithium-ion batteries, which could be smaller, lighter, safer and more efficient if the liquid electrolytes they contain were replaced by solids. A promising candidate for a solid-state electrolyte is a new class of materials based on lithium compounds, presented by physicists from Switzerland and Poland.
Could switchgrass help China's air quality?
Researchers from the United States and China have proposed an idea that could improve China’s air quality, but they’re not atmospheric scientists. They’re agronomists.
“China’s poor air quality is caused by a combination of coal burning and particulates from soil erosion. The Loess Plateau is the major source of erosion in China, and air quality there is just terrible. If erosion in the Loess Plateau can be improved, air quality will improve,” says D.K. Lee, an agronomist in the Department of Crop Sciences at the University of Illinois.
Massive Antarctic Volcanic Eruptions Triggered Abrupt Southern Hemisphere Climate Changes Near the End of the Last Ice Age
New findings published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) by Desert Research Institute (DRI) Professor Joseph R. McConnell, Ph.D., and colleagues document a 192-year series of volcanic eruptions in Antarctica that coincided with accelerated deglaciation about 17,700 years ago.
What Happens to the Antarctic Ocean with 1 Degrees Celsius of Warming?
Scientists have discovered “massive impacts” on marine life in the Antarctic Ocean when waters are warmed by 1 degree Celsius, including a doubling in growth of some species and a drop in overall biodiversity, according to a new study in the journal Current Biology.