While Hurricane Irma moves through the Caribbean islands toward South Florida with sustained winds of 185 miles per hour, forecasters are warning that two other major named storms have formed in the Atlantic Basin — Hurricanes Katia and Jose. It is the first time since 2010 that three hurricanes have been active in the region at the same time.
articles
Monarch butterflies disappearing from western North America
Monarch butterfly populations from western North America have declined far more dramatically than was previously known and face a greater risk of extinction than eastern monarchs, according to a new study in the journal Biological Conservation.
“Western monarchs are faring worse than their eastern counterparts,” said Cheryl Schultz, an associate professor at Washington State University Vancouver and lead author of the study. “In the 1980s, 10 million monarchs spent the winter in coastal California. Today there are barely 300,000.”
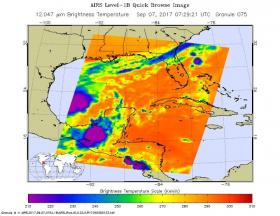
Satellites Show Hurricane Katia Not Moving Much
Satellite imagery from NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites showed that Hurricane Katia had not moved much, just about 30 miles in 16 hours.
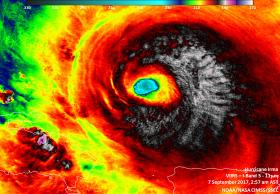
Satellites Show Different Sides of Hurricane Irma
Satellite imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite and NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite have provided different data on the still Category 5 Hurricane Irma as it headed for the Turks and Caicos Islands.
Ship Exhaust Makes Oceanic Thunderstorms More Intense
Thunderstorms directly above two of the world’s busiest shipping lanes are significantly more powerful than storms in areas of the ocean where ships don’t travel, according to new research.
IBM and MIT to pursue joint research in artificial intelligence, establish new MIT–IBM Watson AI Lab
IBM and MIT today announced that IBM plans to make a 10-year, $240 million investment to create the MIT–IBM Watson AI Lab in partnership with MIT. The lab will carry out fundamental artificial intelligence (AI) research and seek to propel scientific breakthroughs that unlock the potential of AI. The collaboration aims to advance AI hardware, software, and algorithms related to deep learning and other areas; increase AI’s impact on industries, such as health care and cybersecurity; and explore the economic and ethical implications of AI on society. IBM’s $240 million investment in the lab will support research by IBM and MIT scientists.