A new study suggests that nations have a bit more time than previously thought if they want to cut greenhouse gas emissions and limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit). The research, published in the journal Nature Geoscience, finds that the world’s economies can emit an additional 700 billion tons of carbon dioxide before exceeding 1.5 degrees — more than twice previous estimates.
articles
Fly away home? Ice age may have clipped bird migration
The onset of the last ice age may have forced some bird species to abandon their northerly migrations for thousands of years, says new research led by a University of Nebraska-Lincoln ornithologist.
Wave Glider surfs across stormy Drake Passage in Antarctica
The Southern Ocean is key to Earth’s climate, but the same gusting winds, big waves and strong currents that are important to ocean physics make it perilous for oceanographers.
Could Condors Return to Northern California?
A study of lead exposure indicates condors could one day return to Northern California.
WSU researchers see popular herbicide affecting health across generations
First, the good news. Washington State University researchers have found that a rat exposed to a popular herbicide while in the womb developed no diseases and showed no apparent health effects aside from lower weight.
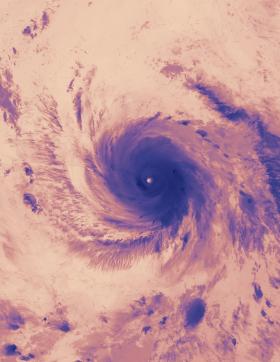
NASA Finds Very Heavy Rainfall in Hurricane Maria
NASA looked into Hurricane Maria and found that powerful convective storms within the hurricane were dropping heavy rainfall. Maria brought that heavy rainfall to Puerto Rico and made landfall on Sept. 20 at 6:15 a.m. EDT.