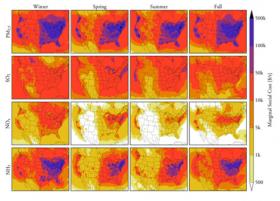
At Carnegie Mellon, Professor Peter Adams is working to make sure that everyone who is affected by air pollution has the tools they need to understand the quality of their air. When we talk about studying air pollution, we typically think of official government agencies and university labs, measuring particles and tracking wind speed—and with good reason. Until very recently, modeling the movement of pollution in the air required very complex calculations—models that often took days and even weeks to run. But air quality affects everyone: not just governments and universities, but average citizens, children, pets. At Carnegie Mellon, Civil and Environmental Engineering (CEE) and Engineering and Public Policy (EPP) Professor Peter Adams is working to make sure that everyone who is affected by air pollution has the tools they need to understand the quality of their air.
articles
Emerging Disease Further Jeopardizes North American Frogs
A deadly amphibian disease called severe Perkinsea infections, or SPI, is the cause of many large-scale frog die-offs in the United States, according to a new study by the U.S. Geological Survey.
Frogs and salamanders are currently among the most threatened groups of animals on the planet. The two most common frog diseases, chytridiomycosis and ranavirus infection, are linked to frog population declines worldwide. The new study suggests that that SPI is the third most common infectious disease of frogs.
New Method to Estimate Abundance, Detect Trends in North Atlantic Right Whales Confirms Recent Population Decline
NOAA Fisheries researchers and colleagues at the New England Aquarium have developed a new model to improve estimates of abundance and population trends of endangered North Atlantic right whales, which have declined in numbers and productivity in recent years. The findings were published in the journal Ecology and Evolution.
End-of-Summer Arctic Sea Ice Extent Is Eighth Lowest on Record
Arctic sea ice appeared to have reached its yearly lowest extent on Sept. 13, NASA and the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado Boulder have reported. Analysis of satellite data by NSIDC and NASA showed that at 1.79 million square miles (4.64 million square kilometers), this year’s Arctic sea ice minimum extent is the eighth lowest in the consistent long-term satellite record, which began in 1978.
Rebuilding from 2011 Earthquake, Japanese Towns Choose to Go Off the Grid
Many of the cities in northern Japan damaged by the 2011 earthquake and tsunami are building back their electric grids with renewable energy and micro-grids — bucking the nation’s old, centralized utility system by making communities in the region self-sufficient in generating electricity, Reuters reported.
Gulf Spill Oil Dispersants Associated with Health Symptoms in Cleanup Workers
Workers who were likely exposed to dispersants while cleaning up the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill experienced a range of health symptoms including cough and wheeze, and skin and eye irritation, according to scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH). The study appeared online Sept. 15 in Environmental Health Perspectives and is the first research to examine dispersant-related health symptoms in humans.