Australian scientists have paved the way for carbon neutral fuel with the development of a new efficient catalyst that converts carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air into synthetic natural gas in a ‘clean’ process using solar energy.
articles
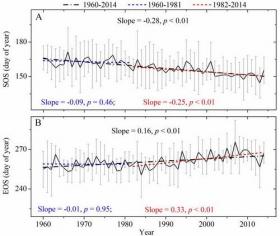
New Perspective: Vegetation Phenology Variability Based on Tibetan Plateau Tree-ring Data
How vegetation phenology on the Tibetan Plateau (TP), the earth's largest surface area above 4000 m ASL, responds to climate change, in particular to rising temperatures, has attracted much attention in recent years. An increase in growth activity of high-elevation vegetation on the TP may have a considerable impact on the regional carbon budget.
Cities Fight Climate Change Through Ecosystem Restoration
Flooding and extreme heat are projected to increase over the next few decades and will be extremely costly to manage. But a new study from Simon Fraser University shows how cities working together to restore and maintain ecosystems can be cheaper than building hard infrastructure to respond to climate change, and provides additional benefits such as buoyant property values and community health.
Wild monkeys use loud calls to assess the relative strength of rivals
Gelada males—a close relative to baboons—pay attention to the loud calls of a rival to gain information about his relative fighting ability compared to themselves, a new study indicated.
Vibrations can be bad for farmers' backs
Researcher Catherine Trask and recent master’s graduate Xiaoke Zeng have found that farmers experience prolonged “body shock” when riding horses or driving farming machinery on uneven terrain during an average workday. Whole body vibration is a major risk factor for developing back pain, they say.
“Farmers are often unaware that body vibration from machinery use is a potentially harmful physical hazard,” said Trask, U of S Canada Research Chair in Ergonomics and Musculoskeletal Health
Deceleration of runaway electrons paves the way for fusion power
Fusion power has the potential to provide clean and safe energy that is free from carbon dioxide emissions. However, imitating the solar energy process is a difficult task to achieve. Two young plasma physicists at Chalmers University of Technology have now taken us one step closer to a functional fusion reactor. Their model could lead to better methods for decelerating the runaway electrons, which could destroy a future reactor without warning.