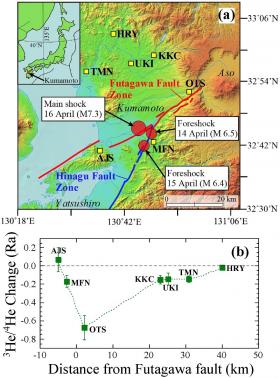
Researchers at the University of Tokyo and their collaborators have revealed a relationship between helium levels in groundwater and the amount of stress exerted on inner rock layers of the earth, found at locations near the epicenter of the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake. Scientists hope the finding will lead to the development of a monitoring system that catches stress changes that could foreshadow a big earthquake.
Several studies, including some on the massive earthquake in Kobe, Japan, in 1995, have indicated that changes to the chemical makeup of groundwater may occur prior to earthquakes. However, researchers still needed to accumulate evidence to link the occurrence of earthquakes to such chemical changes before establishing a strong correlation between the two.