Lowly sawdust, the sawmill waste that’s sometimes tossed onto home garage floors to soak up oil spilled by amateur mechanics, could receive some new-found respect thanks to science. Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory have chemically modified sawdust to make it exceptionally oil-attracting and buoyant, characteristics that are ideal for cleaning oil spills in the icy, turbulent waters of the Arctic. The nontoxic material absorbs up to five times its weight in oil and stays afloat for at least four months.
articles
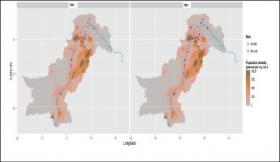
Millions exposed to mercury in urban Pakistan
More than 40 per cent of Pakistanis living in urban areas are exposed to mercury contamination through dust particles and bioaccumulation, says a new study.
The study, published last month (November) in Science of the Total Environment, amassed hair samples from 22 sites in five zones in Pakistan — Swat Valley & Gilgit-Baltistan regions, Kashmir Valley, Lower Himalaya Mountains and Indus Plains.
7 Sustainable Holiday Gift Ideas
Tis the season, and we all are buying gifts. The question is how to do so without saddling friends and families with returns, throwaway gift paper or mounds of fattening desserts.
Here are seven gift ideas that show you care for not only the person receiving the gift, but also for people and planet.
1. Make a donation
This is my favorite gift. I give to a charity that I think aligns with the gift recipient’s passions. Does she love dogs? A gift in her name to the humane society always results in a truly genuine positive response. What family is not touched by health issues like heart disease or cancer? A gift to the Heart Association or Cancer Society is a thoughtful and meaningful way of saying you care. Looking for a charity? I use Charity Navigator to find credible nonprofits. The site also has top 10 lists that cover a diverse range of charities.
Study shows wheat crop yield can be increased by up to 20% using new chemical technology
UK scientists have created a synthetic molecule that, when applied to crops, has been shown to increase the size and starch content of wheat grains in the lab by up to 20%.
The new plant application, developed by Rothamsted Research and Oxford University, could help solve the issue of increasing food insecurity across the globe. Some 795 million people are undernourished, and this year's El Nino has shown how vulnerable many countries are to climate-induced drought.
Researchers Solve Mystery Of Historic 1952 London Fog And Current Chinese Haze
Few Americans may be aware of it, but in 1952 a killer fog that contained pollutants covered London for five days, causing breathing problems and killing thousands of residents. The exact cause and nature of the fog has remained mostly unknown for decades, but an international team of scientists that includes several Texas A&M University-affiliated researchers believes that the mystery has been solved and that the same air chemistry also happens in China and other locales.
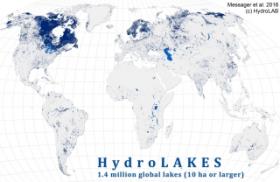
Taking stock of the world's lakes - New global database
The total shoreline of the world’s lakes is more than four times longer than the global ocean coastline. And if all the water in those lakes were spread over the Earth’s landmass, it would form a layer some four feet (1.3 metres) deep.
Those are just two of the big-picture findings to emerge from the most complete global database of lakes to date, compiled by geographers at McGill University. Their research, published in Nature Communications, promises to help scientists better understand the important role of lakes in the Earth’s complex environmental systems – from the hydrological cycle and weather patterns, to the transport, distribution or storage of pollutants and nutrients through the landscape.