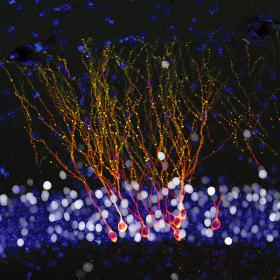
- Even a mild rise in temperature damages insect’s ability to reproduce
- Insect populations in high latitude countries are worst affected
- Identifying genes linked to increased and decreased reproduction may help understand how insects cope with climate change and controlling insect pests
With 2016 reportedly the warmest year on record, scientists have discovered insects are already feeling the effects of climate change, as a rise in temperature is shown to damage their ability to reproduce.