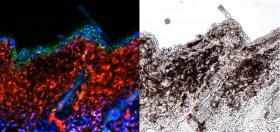
Melanoma, a cancer of skin pigment cells called melanocytes, will strike an estimated 87,110 people in the U.S. in 2017, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
articles
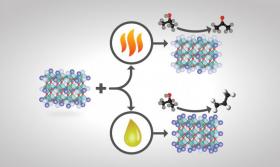
Researchers Customize Catalysts to Boost Product Yields, Decrease Chemical Separation Costs
For some crystalline catalysts, what you see on the surface is not always what you get in the bulk, according to two studies led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Living Mulch Builds Profits, Soil
Living mulch functions like mulch on any farm or garden except — it’s alive. No, it’s not out of the latest horror movie; living mulch is a system farmers can use to benefit both profits and the soil. While the system has been around for a while, scientists at the University of Georgia are making it more efficient and sustainable.
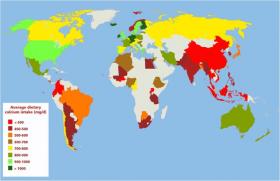
Global Calcium Consumption Appears Low, Especially in Asia
Daily calcium intake among adults appears to vary quite widely around the world in distinct regional patterns, according to a new systematic review of research data ahead of World Osteoporosis Day on Friday, Oct. 20.
DNA Tests on Albatross Poo Reveal Secret Diet of Top Predator
A study that used DNA tests to analyse the scats of one of the world’s most numerous albatrosses has revealed surprising results about the top predator’s diet.
Nice Ice, Maybe? Husker Research Finds Ice Removal Can Be a Breeze
Water-repellent surfaces and coatings could make ice removal a literal breeze by forcing ice to grow up rather than just skate by, says a new study from the University of Nebraska-Lincoln and several Chinese institutions.