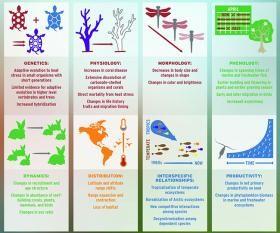
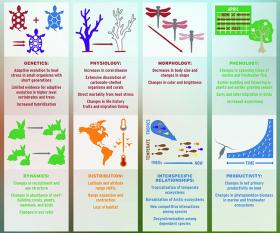
El cambio climático ya ha afectado a casi todos los aspectos de la vida en la tierra, según un nuevo estudio en la revista Science. La elevación de las temperaturas globales ha alterado todo, desde ecosistemas enteros hasta los genes individuales de las especies.
articles
Just 1 Degree C of Warming Has Altered Nearly Every Aspect of Life on Earth
Climate change has already impacted nearly every aspect of life on earth, according to a new study in the journal Science. Warming global temperatures have altered everything from entire ecosystems down to the individual genes of species.
¿Quién influye en las negociaciones sobre el clima?
La influencia de las corporaciones que lucran con combustibles fósiles fue fuertemente cuestionada por los países en desarrollo en la reunión posterior a París de las negociaciones sobre el cambio climático en Bonn la semana pasada. Los seguidores del clima Pavlos Georgiadis, Renee Karunungan y Anna Pérez Català destacan las cuestiones clave que se debatieron.
Researchers Develop Novel Approach for Quantifying Nitrate Discharge from Groundwater to Streams
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new way to determine the rate at which nitrate pollution will make its way from groundwater into streams. The work has implications for predicting long-term pollution in groundwater-fed streams.
Nitrate pollution, primarily from fertilizer runoff, is one of the major freshwater contaminants in the United States. Additionally, the pollution persists in aquifers – and thus in groundwater – which feed into streams over a period of years or decades.
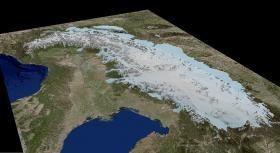
Descongelar el hielo hace crecer los Alpes
Los Alpes están "creciendo" constantemente alrededor de uno a dos milímetros por año. Asimismo, los antiguos subcontinentes glaciares de Norteamérica y Escandinavia también están experimentando constantes movimientos ascendentes.
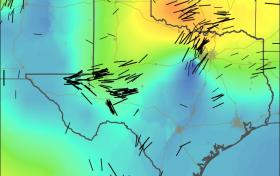
New maps reveal safe locations for wastewater injection
Stanford geophysicists have compiled the most detailed maps yet of the geologic forces controlling the locations, types and magnitudes of earthquakes in Texas and Oklahoma.
These new “stress maps,” published in the journals Geophysical Research Letters and Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, provide insight into the nature of the faults associated with recent temblors, many of which appear to have been triggered by the injection of wastewater deep underground.
“These maps help explain why injection-induced earthquakes have occurred in some areas, and provide a basis for making quantitative predictions about the potential for seismic activity resulting from fluid injection,” said study co-author Mark Zoback, the Benjamin M. Page Professor of Geophysics in Stanford’s School of Earth, Energy & Environmental Sciences.