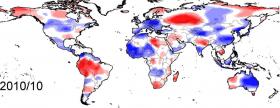
The rapidly growing wind energy industry may be challenged by changes in locations of wind resources
articles
Scientists unveil new satellite-based global drought severity index
Enhanced monitoring tool adds groundwater storage to assessment factors
U of T neuroscientist on how advances in AI may help us better understand why neurons are shaped the way they are
The shape of our neurons may indicate our brains actually employ a type of learning, dubbed “deep learning,” that was developed to drive artificial intelligence, or AI, applications, a University of Toronto researcher has found.
Sustainable dams – are they possible?
Humans have been altering natural waterways for centuries, but only in the last several decades have dams raised ecological concerns.
N. LeRoy Poff, professor of biology at Colorado State University, studies the ecological impact to rivers from human-caused changes, such as dam building, and how these modified river systems can be managed for resilience.
Canola Oil Linked to Worsened Memory and Learning Ability in Alzheimer's Disease, Temple Researchers Report
Canola oil is one of the most widely consumed vegetable oils in the world, yet surprisingly little is known about its effects on health. Now, a new study published online December 7 in the journal Scientific Reports by researchers at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University (LKSOM) associates the consumption of canola oil in the diet with worsened memory, worsened learning ability and weight gain in mice which model Alzheimer’s disease. The study is the first to suggest that canola oil is more harmful than healthful for the brain.
After the fire, charcoal goes against the grain, with the flow
When a forest fire decimated more than 3,000 acres of Rice University-owned timberland in 2011, biogeochemist Carrie Masiello saw a silver lining in the blackened trees.